green water desalination by mohammed sanduk from uk
designer's own words:
Green Water Desalination
Mohammed Sanduk
Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Chemical Engineering Department, CORA, University of Surrey, Guildford Surrey GU2 7XH, UK,
The global oil crisis, the environmental pollutions, and the coming global water crisis implies that alternatives to the conventional desalination plants based on fossil fuels must be developed. Solar desalination is one of the rapidly growing and developed techniques in water treatment field that may face the mentioned challenges.
Solar desalination can be either direct, with collectors and condensers integrated with each other, or indirect, with condensers externally connected to the condensers. Direct solar desalination requires large land areas and has a relatively low productivity compared to the indirect technologies. It is competitive to indirect desalination plants due to its relatively low cost and simplicity.
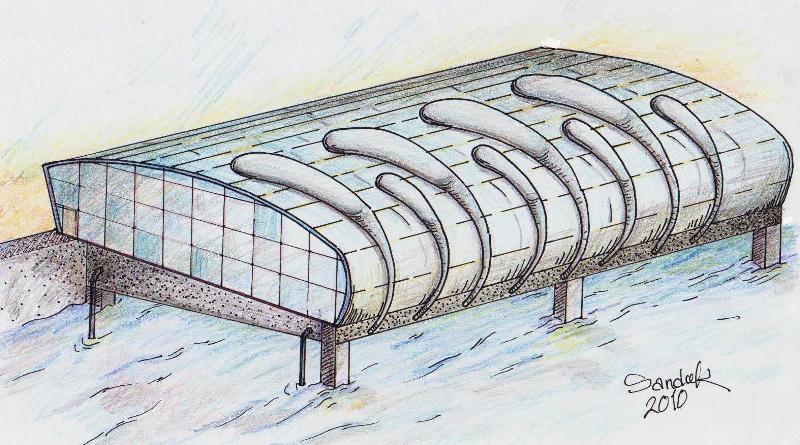
The proposed design is a large architected structure of glass (transparent material) and steel, of a concrete base, constructed along sea side; and over the sea water. There is a gap between the base and the sea level. The base of the structure is a concrete basin, filled by sea water.
The proposed design is for direct solar water desalination, but tries to overcome the low productivity problem, the new design based on two ways of condensation. The first is the condensation on the glass wall as in conventional solar still and the second condensation is inside ducts passing through the seawater in the basin, in addition to the large area of the basin. In this case the efficiency becomes higher. The second process is similar to the Multiple effect distillation (MED) technique.
The proposed design covers length of one kilometer (many sections) along the sea side and of width of twenty meters across the sea.
The main concept depends on the utilization of the sea as a source of vapour inside the structure, and using the sea as well to condense the vapour. This process has no need for energy consuming. The needed energy is only for ventilation extractor fans, lights, and some pumps that may be achieved by using solar PV energy power.
For a normal solar stills of the construction that depends on condensation on the glass, a production rate in the order of 6 litres per day and square meter of collector surface. Accordingly, the proposed structure is of a collecting surface area of about 30000 m2 ( For a length 1km of the sea side, width of 20m and average height 5m ) the estimated product is about 180000 liters (180 m3) per day . In addition to that the condensation of extracted vapour is estimated to be more than 70000 liters (70 m3). The total produced water is more than 250 m3 / day approximately.
The main features of the design are:
1- Free energy desalination.
2- Easy to use technology.
3- Environment friendly.
4- Improvement of the remote and abandoned long sea sides.
5- Low cost of maintenance.
6- Approximately, there are no consuming parts.
7- Easy to control system.
8- A modern architecture site.
The system is quite suitable for countries have sea side and hot weather.
general view of the design
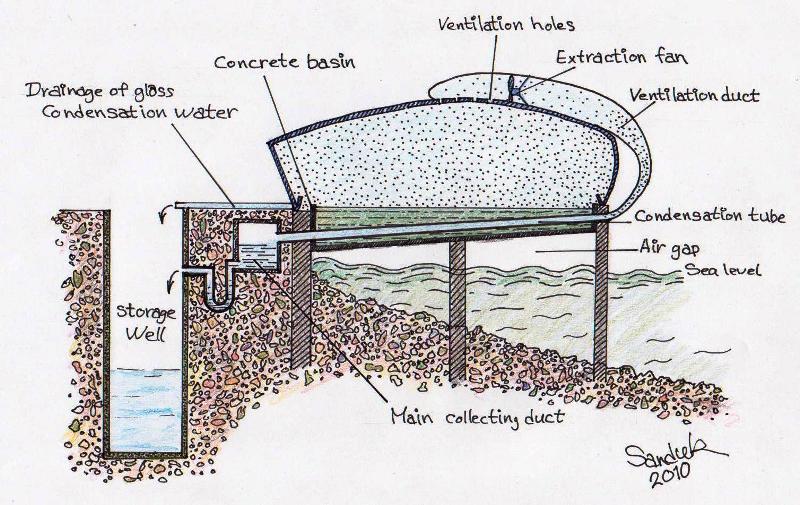 cross section showing the structure of the system
cross section showing the structure of the system